What is a game loop?
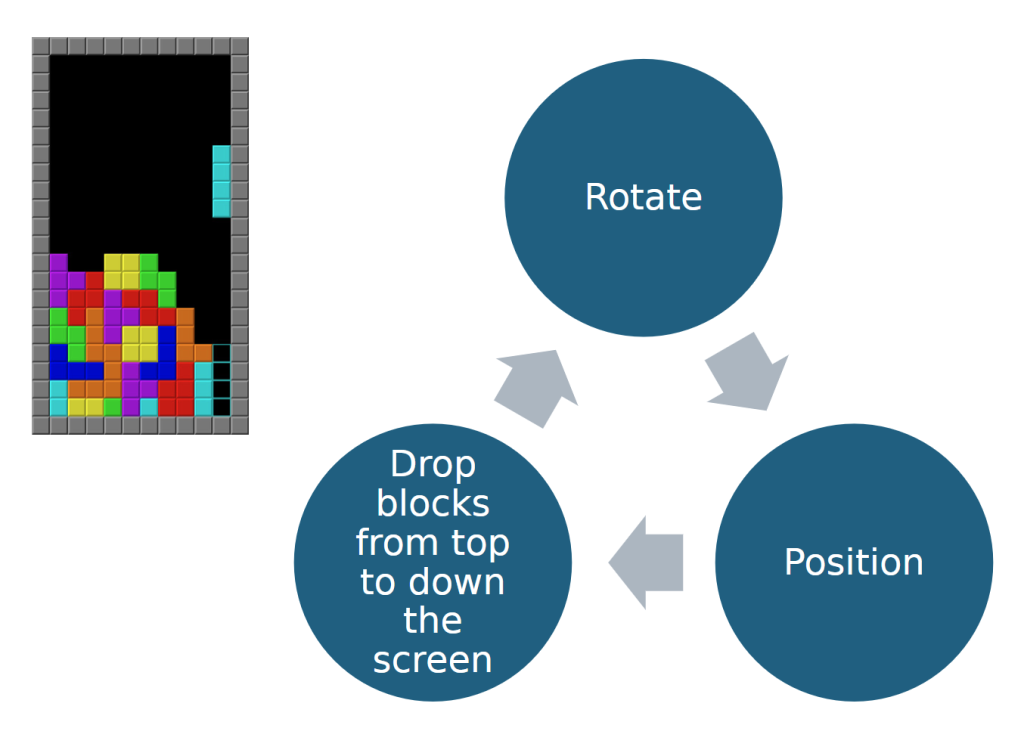
In game design, a gameplay loop refers to a sequence of actions that players repeatedly engage in, forming the core of their gaming experience and encouraging continued play.
These loops can range from simple actions, such as spotting and jumping to avoid obstacles, to more intricate processes like organizing a raid, defeating enemies, and distributing loot.
The core gameplay loop is fundamental, as it serves as the foundation for all other gameplay elements. For instance, in Super Mario, the loop consists of spotting, leaping, surviving, and repeating, while in first-person shooting games, it involves aiming, firing, advancing, and repeating
Strong gameplay loops often develop organically rather than being meticulously planned from the outset, so it’s important not to overthink the simplicity of your initial game mechanics. Starting small, with game mechanics and content built in short increments, helps ensure players clearly understand their actions. It’s typically more effective to create multiple loops independently before trying to interconnect them.
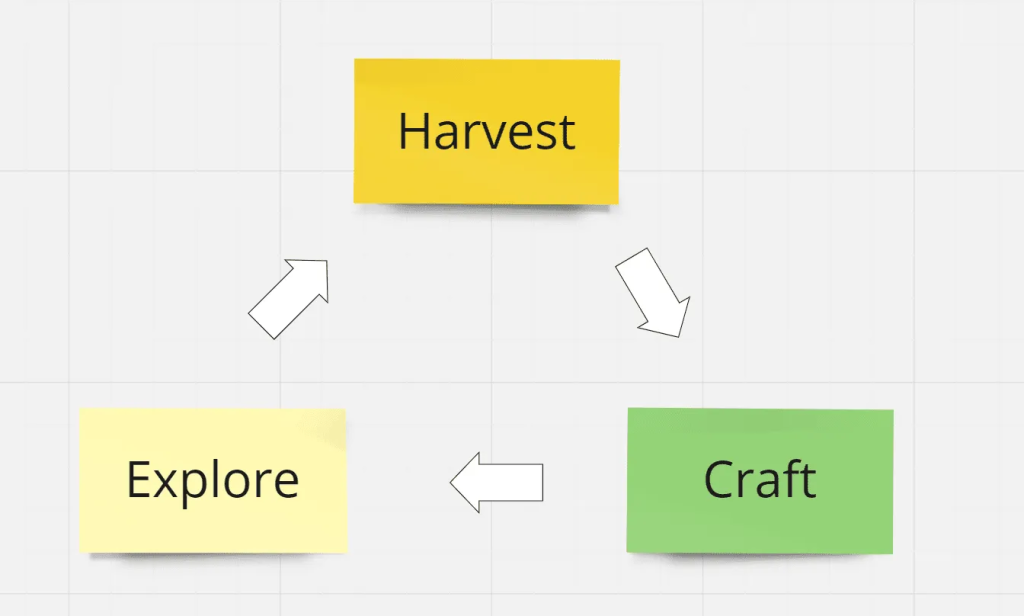
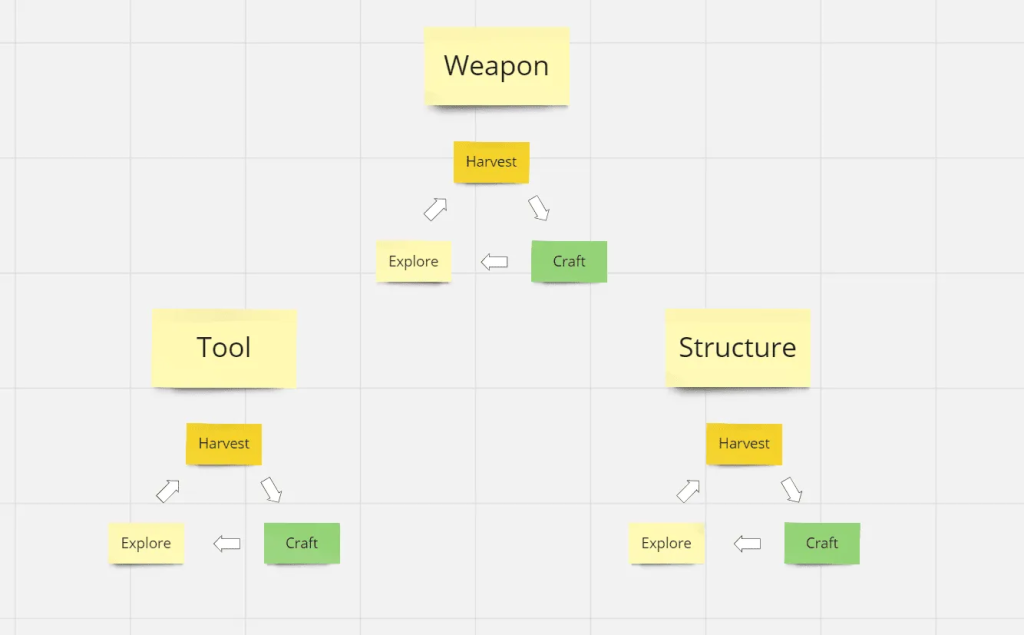
Take Minecraft as an example of a self-directed game loop, which revolves around a simple three-stage process: Explore, Harvest, and Craft. This loop encapsulates the immediate actions players undertake within a single session while also reflecting larger gameplay patterns over time. Players explore their environment to find resources, harvest these materials, and then use them to craft tools or structures, all of which supports their progression within the game.
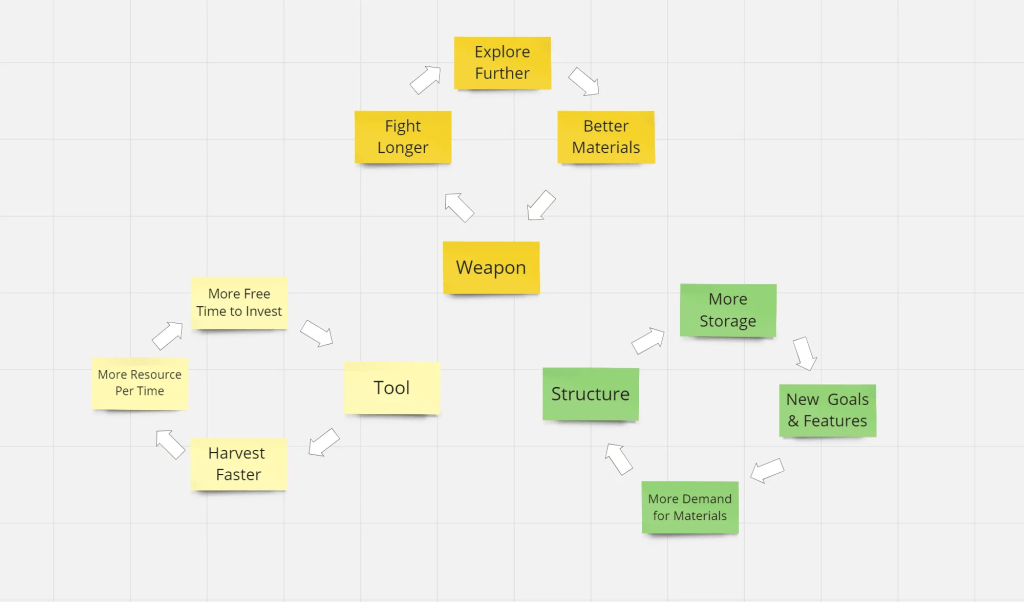
The loop resonates with both individual and group play; players collect resources together and refine them into useful items, fostering community building through gear and infrastructure. As players gain experience and familiarity with their surroundings, they expand their exploration into new biomes, setting self-directed goals that enrich their gameplay.
This gradual increase in comfort and understanding allows players to strategize their objectives and prioritize tasks, leading to nested core loops that enhance long-term engagement—an attribute shared by many successful survival games, including Subnautica. Such dynamics contribute to the enduring appeal and legendary status of these games.

Leave a Reply